Introduction
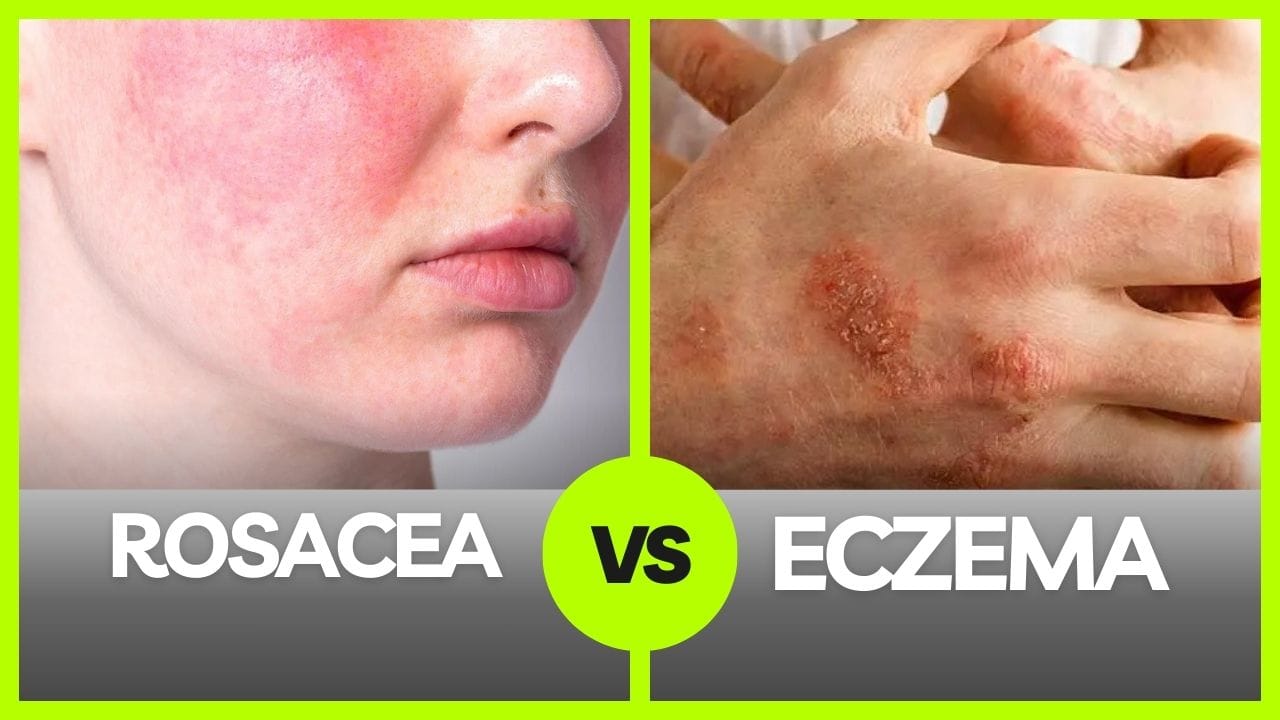
Ever looked at a stubborn red patch on your skin and wondered, “Is this rosacea or eczema?” Don’t worry; you’re not alone! These two conditions might seem alike at first glance, but they’re actually quite different. Knowing the difference between rosacea and eczema is the first step toward treating your skin effectively. Let’s dive into the details.
What Is Rosacea?
Definition and Overview
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, pus-filled bumps. It’s often mistaken for acne or an allergic reaction, but it’s its own unique beast.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause isn’t clear, but genetics, immune system overreactions, and environmental factors play a role.
Common Symptoms
- Persistent facial redness
- Visible blood vessels (telangiectasia)
- Flushing or blushing
- Skin sensitivity
Types of Rosacea
Rosacea isn’t one-size-fits-all. Here are the four main types:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea (ETR): Redness and visible blood vessels dominate.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Think red bumps and pustules—similar to acne.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Leads to thickened, bumpy skin, usually on the nose.
- Ocular Rosacea: Eyes get in on the action, causing redness and irritation.
What Is Eczema?
Definition and Overview
Eczema, or dermatitis, is a condition that makes your skin itchy, red, and inflamed. It’s incredibly common and can appear anywhere on the body.
Causes of Eczema
Eczema is often linked to an overactive immune system. Triggers include allergens, irritants, and even stress.
Common Symptoms
- Intense itching
- Red or brownish patches
- Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
- Oozing or crusting
Types of Eczema
Eczema comes in many flavors, each with its quirks:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, often linked to allergies.
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by irritants or allergens.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Tiny, itchy blisters on hands and feet.
- Nummular Eczema: Circular patches of irritated skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Often found where skin is oily, like the scalp.
Key Differences Between Rosacea and Eczema
Differences in Causes
Rosacea’s roots lie in vascular issues and immune responses, while eczema stems from an overactive immune system and a damaged skin barrier.
Differences in Symptoms
Rosacea focuses on facial redness and bumps, whereas eczema features intense itching and widespread irritation.
Differences in Affected Areas
Rosacea sticks to your face, while eczema can show up anywhere—from your hands to your elbows.
Differences in Triggers
Triggers for rosacea include spicy foods, alcohol, and heat. Eczema, on the other hand, flares up with allergens, harsh soaps, or even stress.
Diagnosing Rosacea and Eczema
How Dermatologists Identify Rosacea
A dermatologist will assess symptoms like facial redness, visible vessels, and skin texture.
How Eczema Is Diagnosed
Eczema diagnosis involves examining your skin and sometimes allergy testing.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
Topical Treatments
Common treatments include azelaic acid, metronidazole, or ivermectin.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
Avoiding triggers like sunlight and spicy foods can make a big difference.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Medications
Topical corticosteroids and antihistamines are often prescribed.
Moisturizers and Skincare Routine
Keeping your skin hydrated is key to preventing flare-ups.
Managing and Living With Rosacea and Eczema
Living with rosacea and eczema can be challenging, but understanding these conditions and implementing effective management strategies can significantly improve quality of life. Below, you’ll find a guide to help navigate these skin conditions:
Triggers to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding triggers can help minimize flare-ups:
Fragranced skincare products.
Common Triggers for Rosacea:
Spicy foods and alcohol.
Sun exposure and extreme temperatures.
Stress and emotional triggers.
Common Triggers for Eczema:
Harsh soaps and detergents.
Allergens like dust mites or pet dander.
Skincare Tips
- For Rosacea:
- Use a gentle, fragrance-free cleanser.
- Apply sunscreen with SPF 30+ daily to protect against UV rays.
- Opt for green-tinted moisturizers to neutralize redness.
- For Eczema:
- Keep the skin hydrated with thick emollients or ointments.
- Use lukewarm water for bathing and avoid long showers.
- Pat skin dry instead of rubbing with a towel.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet:
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts.
- Avoid known allergens or food triggers.
- Stress Management:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to reduce flare-ups triggered by stress.
- Engage in physical activities like yoga or walking.
- Environment:
- Use a humidifier in dry climates to prevent skin dryness.
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton.
Managing and Living With Rosacea and Eczema
Living with rosacea and eczema can be challenging, but understanding these conditions and implementing effective management strategies can significantly improve quality of life. Below, you’ll find a guide to help navigate these skin conditions:
Understanding Rosacea and Eczema
- Rosacea: A chronic skin condition that causes redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes acne-like bumps, primarily on the face.
- Eczema: Also known as atopic dermatitis, it’s a condition that leads to dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, often appearing on the hands, face, or behind the knees.
While both conditions are distinct, they share common triggers and require careful skin care routines.
Triggers to Avoid
Identifying and avoiding triggers can help minimize flare-ups:
- Common Triggers for Rosacea:
- Spicy foods and alcohol.
- Sun exposure and extreme temperatures.
- Stress and emotional triggers.
- Common Triggers for Eczema:
- Harsh soaps and detergents.
- Allergens like dust mites or pet dander.
- Fragranced skincare products.
Skincare Tips
- For Rosacea:
- Use a gentle, fragrance-free cleanser.
- Apply sunscreen with SPF 30+ daily to protect against UV rays.
- Opt for green-tinted moisturizers to neutralize redness.
- For Eczema:
- Keep the skin hydrated with thick emollients or ointments.
- Use lukewarm water for bathing and avoid long showers.
- Pat skin dry instead of rubbing with a towel.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet:
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts.
- Avoid known allergens or food triggers.
- Stress Management:
- Practice mindfulness or meditation to reduce flare-ups triggered by stress.
- Engage in physical activities like yoga or walking.
- Environment:
- Use a humidifier in dry climates to prevent skin dryness.
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics like cotton.
Medical Treatments
If lifestyle adjustments and skincare aren’t enough, consult a dermatologist.
- For Rosacea:
- Prescription creams or gels containing metronidazole or azelaic acid.
- Laser therapy for reducing redness and visible blood vessels.
- For Eczema:
- Topical corticosteroids for severe flare-ups.
- Immunomodulators or biologics for chronic cases.
Emotional Support
Living with visible skin conditions can affect mental health.
- Join Support Groups: Connecting with others can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- Professional Counseling: Therapists can help with self-esteem or anxiety issues linked to these conditions.
When to See a Dermatologist
For Eczema:
- Severe Itching and Redness
If your eczema causes persistent itching, redness, or swelling that disrupts your daily life or sleep. - Unresponsive to Over-the-Counter Treatments
If moisturizers, hydrocortisone cream, or other OTC options don’t improve your symptoms. - Recurring Flare-Ups
When flare-ups occur frequently despite following a skincare routine and avoiding triggers. - Skin Infections
Signs of infection like pus, oozing, crusting, or increased pain, heat, or swelling in the affected area. - Impact on Mental Health
If the appearance of eczema or its symptoms lead to anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem.
For Rosacea:
- Persistent Redness or Flushing
If redness on your cheeks, nose, or forehead persists and is not improving with basic skincare adjustments. - Visible Blood Vessels or Bumps
When blood vessels become visible or you experience pimple-like bumps on your face. - Eye Involvement (Ocular Rosacea)
If your eyes are red, irritated, or sensitive to light, or you experience blurred vision. - Burning or Stinging Sensations
If you feel discomfort like burning or stinging, especially when applying skincare products. - Worsening Symptoms or Emotional Distress
When rosacea starts to significantly affect your confidence or quality of life.
Why See a Dermatologist?
A dermatologist can:
- Provide a tailored treatment plan with prescription medications like topical steroids, antihistamines, or antibiotics.
- Recommend advanced treatments like light therapy, laser treatments, or biologics.
- Help identify triggers and suggest lifestyle modifications to prevent flare-ups.
Early consultation can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Don’t hesitate to seek expert advice!
Final Thoughts on Rosacea and Eczema
While rosacea and eczema might look similar at first glance, understanding their unique characteristics helps you take control of your skin. With the right diagnosis and treatment, you can manage these conditions effectively.
FAQs
- What’s the biggest difference between rosacea and eczema?
Rosacea primarily affects the face with redness and bumps, while eczema can appear anywhere and causes intense itching. - Can someone have both rosacea and eczema?
Yes, it’s possible to have both, but they require different treatments. - Are rosacea and eczema hereditary?
Genetics can play a role in both conditions, but environmental factors also contribute. - How do I know if my skin condition is serious?
If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, consult a dermatologist. - Can lifestyle changes completely cure rosacea or eczema?
While they can’t be cured, lifestyle changes significantly reduce flare-ups and improve quality of life.
Read more article here.